HEPA 1-6:肝细胞癌的小鼠模型
肝细胞癌(HCC)是一种激进的恶性肿瘤,逐渐增加了世界范围内的一百万人,目前是世界上癌症相关死亡的第三个主要原因。[1,2]由于乙型肝炎和C病毒的高流行性,HCC的普遍率在亚洲和非洲中最高,这强烈易于达到慢性肝病和随后的HCC的发展。[1]In the Western population, hepatitis C, alcoholic cirrhosis, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) are the main underlying causes. While early stage HCC treatment options include surgical excision, liver transplantation, chemo/radio embolization and radiofrequency ablation, the standard of care for advanced HCC is targeted therapies (sorafenib and regorafenib), radiation and chemotherapy (doxorubicin, 5-FU, and cisplatin).[3]Many clinical trials are underway for unresectable or advanced stage HCC with mono or combination immunotherapy, monoclonal antibodies or oncolytic virus therapy.[1-4]这些疗法表明肿瘤收缩和提高存活率,但没有治疗治疗结果,这些治疗结果或在肝炎,肝硬化或非酒性脂肪肝疾病(NAFLD)如肝炎,肝硬化或非酒精脂肪肝疾病(NAFLD)上的治疗结果。因此,需要增加更好的治疗方案。为了评估在临床前平台中的新颖疗法,Covance建立了同工HCC模yaboapp体育官网型HEPA 1-6。
HEPA 1-6是衍生自BW7756肝癌肿瘤的鼠肝癌,其在C57L / J小鼠中自发地产生,其与最常见的肝癌模型(BNL,A.7R.1,MH-129,MH134和MH-129A)形成鲜明对比是化学转化的或诱导的线。在免疫活性小鼠中建立的HEPA 1-6肿瘤模型代表了免疫疗法的临床前测试临床相关模型。yaboapp体育官网
在这个模型中,我们存在in vivoHEPA 1-6肿瘤模型生长动力学的数据;随着响应单独的检查点抑制剂或与局灶性辐射组合。我们在父母C57L / J菌株中测试了模型(杰克逊实验室,Bar Harbor,Me)和更容易获得的组织互相组织的C57BL / 6菌株。
HEPA 1-6增长参数
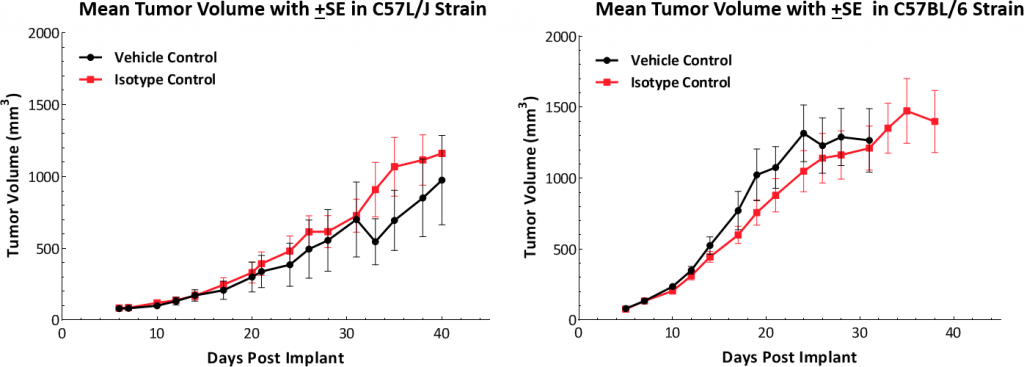
Growth kinetics followingsubcutaneous植入物表明该模型成功地建立了两种鼠标株(图1)。肿瘤的中位数倍增时间为〜5-6天,没有不利的体重变化(数据未显示)。这种稳定的增长率允许三周治疗窗口评估抗肿瘤反应。
HEPA 1-6肿瘤免疫剖面
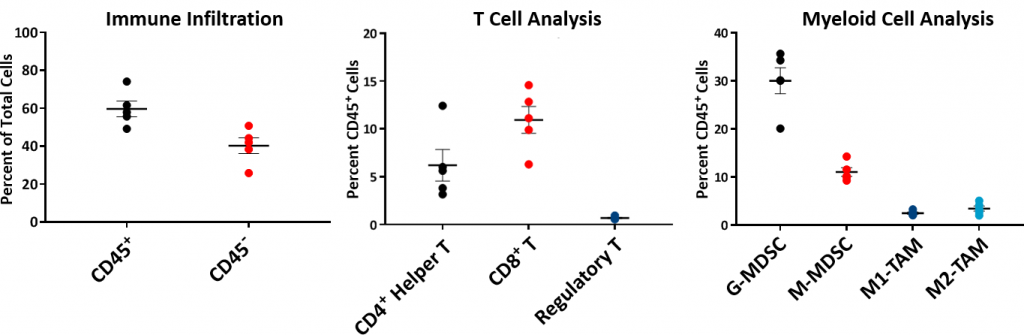
要理解HEPA 1-6肿瘤的免疫分布,分析了基线免疫组合物flow cytometry并且如图2所示。从C57L / J毒株中生长的五个未处理的HEPA 1-6肿瘤建立了免疫曲线至〜750-1000mm3.体积。肿瘤具有相对高的CD45+细胞群(平均〜60%),其中T淋巴细胞(CD8+T细胞和CD4+T helper cells) were moderately represented (mean ~11% and ~6%, respectively). The myeloid population was represented predominantly by G-MDSC (mean ~30%) followed by M-MDSC (mean ~11%). The CD8+肿瘤微环境内的T细胞浸润是暗示免疫响应或“温热”肿瘤模型的暗示。
HEPA 1-6响应检查点抑制剂
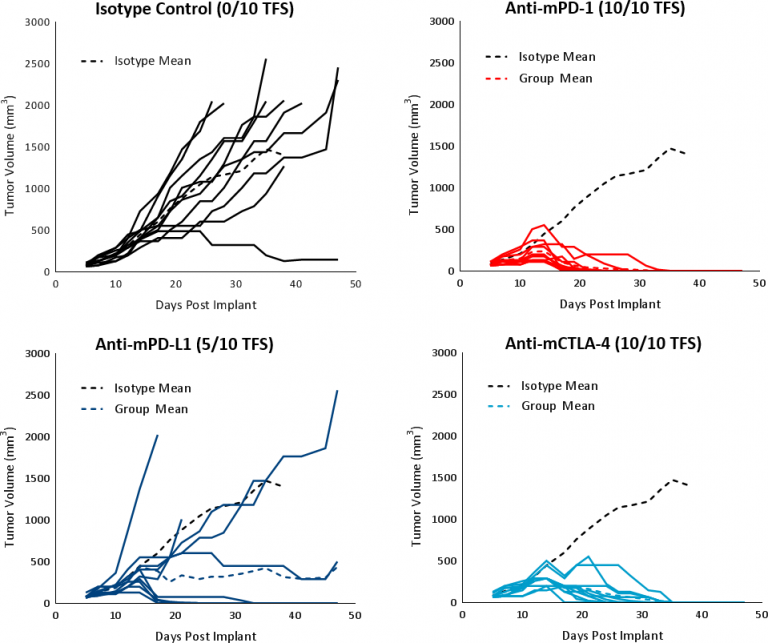
在已建立的肿瘤轴承中评估HEPA 1-6对免疫调节剂的反应(平均肿瘤体积〜100mm3.) C57BL/6 mice treated with checkpoint blockade antibodies (anti-mPD-1, anti-mPD-L1, and anti-mCTLA-4). The controls, vehicle (PBS) and isotype (Rat IgG2b clone LTF-2), showed comparable growth kinetics (Fig. 1). Single agent checkpoint inhibitors anti-mPD-1 and anti-mCTLA-4 elicited a strong response leading to complete tumor regression (CR) and 100% tumor free survivors (TFS). Anti-mPD-L1 treatment also produced a good response in a subset of animals resulting in CR and 5/10 TFS (Fig 3). Treatment with checkpoint inhibitor antibodies was not associated with any significant body weight changes relative to control animals (data not shown). The response to immunotherapy strongly supports the characterization of Hepa 1-6 tumors as immunologically “hot.”
Response to Focal Radiation
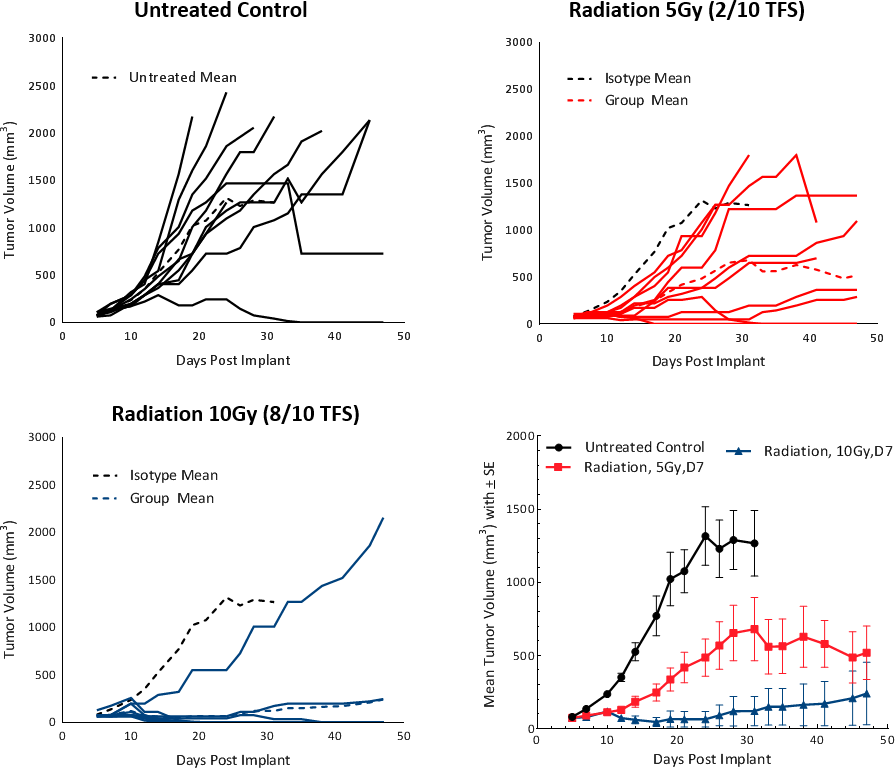
Clinically, patients with non-metastatic HCC receive one or more liver directed therapy (LDT) such as radiotherapy (RT) or stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT).[5]RT可以导致肿瘤收缩并改变肿瘤微环境,以良好的肿瘤抑制Milieu。要测试HEPA 1-6肿瘤至室温的响应,我们使用小动物辐射研究平台(SARRP; Xstrahl)来提供焦点辐射到有针对性的地区。在C57BL / 6小鼠中,在皮下HEPA 1-6肿瘤上测试5和10Gy的焦点辐射剂量。治疗显示剂量依赖性反应,导致> 20天肿瘤生长延迟(TGD)和肿瘤自由幸存者(分别为2/10和8/10)(图4)。剂量为5Gy提供了一种适度的单一疗法反应,寿命增加,建议未来组合研究。
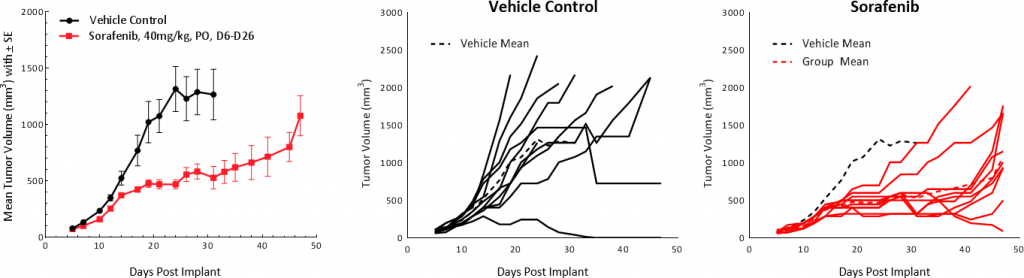
HEPA 1-6回应索拉非尼
索拉非尼,multi-tyrosine激酶抑制剂blocks the activity of Raf kinase, Src, VEGF and PDGF receptors, used as first line treatment in HCC patients, was tested on Hepa 1-6 tumors. Treatment resulted in tumor growth delay of 25.4 days and extended overall survival but resulted in no TFS (Fig 5). These results are comparable to outcomes from clinical studies which showed partial response extending median overall survival from 7.9 months in the control group to 10.7 months in the treated group.[1]
这些初步数据表明,HCC的HEPA 1-6模型具有良好的免疫曲线,可以作为稳健的临床前yaboapp体育官网immuno-oncology模型。我们的数据支持使用该模型在调查免疫治疗剂作为单一疗法或与辐射,小分子,护理标准和其他新的治疗剂组合。请联系人与我们的科学家们谈论HEPA 1-6如何用于您的下一次免疫肿瘤学研究。
模型聚光灯|HEPA 1-6:肝细胞癌的小鼠模型(PDF版)
[1]Medavaram,S和张Y,2018.新兴肝细胞癌中的疗法。Exp Hematol oncol 7:17。
[2]Llovet JM,Montal R,SIA D和Finn Rs,2018.肝细胞癌的分子疗法和精密药。NAT REV CLIN incol。DOI:10.1038 / S41571-018-0073-4。[epub领先] pmid:30061739。
[3]Pinter M & Peck-Radosvljevic M. 2018. Review article: systemic treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. 2018. Aliment Pharmacol Thera, Jul 23. doi: 10.1111/apt.14913. [Epub ahead of print] Review. PMID: 30039640.
[4]WAIDMANN O. 2018.肝细胞癌免疫疗法的最新发展。专家意见生物。8月18日(8):905-910。
[5]Chaub SK et al., 2018. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: current trends and controversies. Technology in Cancer Research & Treatments 17:1-19.
注意:研究是根据AAALAC认可的设施中适用的动物福利法规进行的