B16-F10:鼠黑色素瘤模型
皮肤癌包括所有层的癌,具有最常见的基础细胞(BCC)和鳞状细胞癌(SCC)。黑色素瘤和非黑色素瘤皮肤癌症(Merkel Cell Celcoma,Kaposi Sarcoma,皮肤淋巴瘤和其他肉瘤)都不常见。在所有皮肤癌类型中,黑色素瘤是一种严重的皮肤癌,其在黑素细胞中开始,即位于皮肤表皮的底层(Stratum Baseale)中的黑色素产生神经嵴衍生细胞。虽然恶性BCC和SCC很少转移,但另一方面,较少的恶性黑色素瘤是高度侵袭性的,并且迅速地蔓延到身体的其他部位。黑色素瘤存在于许多不同的形状,尺寸和颜色,具有全面的警告标志。[1]
在早期检测到并治疗时,黑色素瘤是可固化的,估计美国患者的98%估计为5年生存率。[2]Once melanoma becomes invasive into the skin or other parts of the body, it is more difficult to treat and can be fatal. The American Cancer Society’s estimates for melanoma in the United States for 2019 are about 192,310 new melanomas diagnosed of which 96,480 cases will be invasive, and about 7,230 people are expected to die of melanoma. The rates of melanoma have been rising rapidly over the past few decades and melanoma is one of the most common cancers in young adults (especially young women). Light skin color is a major risk factor for melanoma which is 20 times more common in whites than in African Americans, although no race is immune. The risk for each person can be affected by several factors including exposure to sun, UV light, moles, previous cancers, genetic and familial factors.
治疗方案依赖于疾病的阶段,肿瘤的位置和患者的整体健康,包括手术切除黑素瘤,免疫疗法,靶向治疗,化疗和辐射。经常使用的单药疗法在B-RAF基因中的靶向突变,C-kit基因和其他异常基因。此外,所有化疗药物如脱酰脲,替替唑胺,Nab-κBlitaxel,顺铂和卡铂都可以使用。对IL-2,IPILIMIMAB(CTLA-4抑制剂)和PEMBROLIZUMAB等免疫疗递等临床试验进行正在进行中,正在积极招募患者。这些免疫调节药也在组合设置以及新辅助方法中进行测试。另外,正在测试黑色素瘤疫苗,III阶段Melanomas的BCG疫苗和溶瘤病毒(T-VEC)。[3]New treatment options are focused on improving quality of life and increasing survival rates for patients with advanced melanoma.
The murine B16 melanoma model is the most commonly used metastatic melanoma model for preclinical studies. At Covance, we have established the syngeneic B16-F10 model to evaluate responses to immuno-oncology agents and support development of novel therapeutics. The B16-F10 cell line was generated as the 10TH.在C57BL / 6小鼠中B16亲本肿瘤系的序列通道亚克隆。[4]In vitro,这些细胞随着上皮形态的粘附群体而生长。In vivo, intradermal implant of B16-F10 cells in C57BL/6 mice results in aggressively growing tumors. Our growth studies show efficient growth kinetics following a range of inocula with a doubling time of approximately 2-3 days (Fig. 1). Control animals stay on study for 20-25 days before they reach euthanasia criteria of excessive tumor burden. This results in a model which can facilitate up to a two-week dosing window for test agents to elicit their anti-tumor activity. While the model itself does not result in reduction of body weight, tumor scabbing, and ulcerations are common clinical symptoms associated with subcutaneous and intradermal B16-F10 tumor growth.
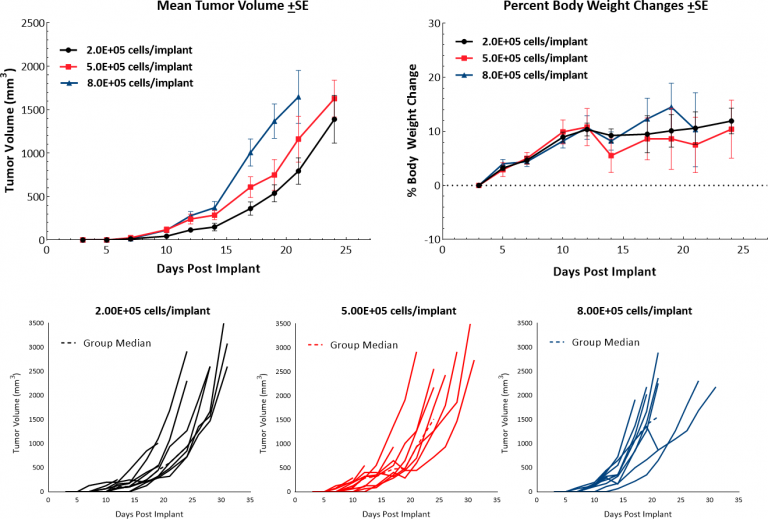
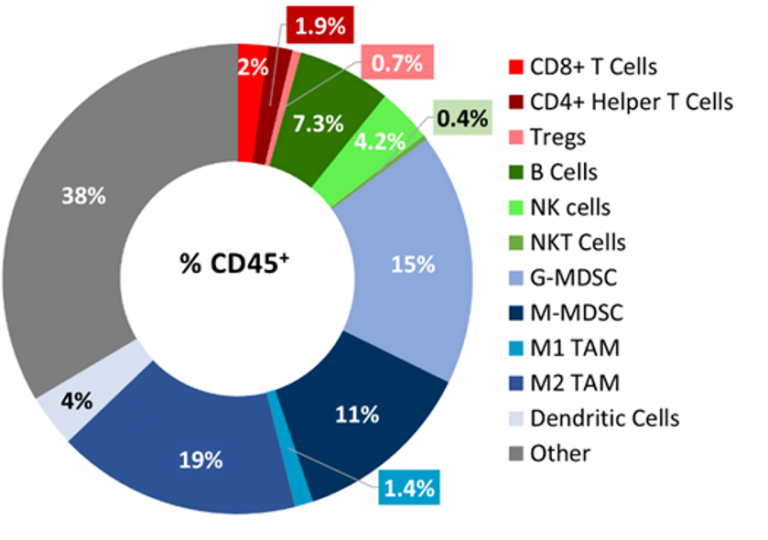
B16-F10肿瘤免疫剖面
B16-F10肿瘤渗透的基线免疫分析flow cytometry5个未经处理的肿瘤(300-500mm3.) and analyzed using the Covance CompLeukocyteTM值package. The immune cell infiltration in the tumor microenvironment, represented a percent of CD45+cells, showed a distinct immune cell population dominated mostly by undefined CD11b+myeloid cells characteristic to this tumor model (Fig 2). The M2 TAMs (19%), G-MDSCs (15%) and M-MDSCs (11%) were represented in relatively proportionate extents while M1 TAMs (1.4%) and dendritic cell (4%) populations were minimally represented. The lymphoid population was mostly comprised of B (7.3%) and NK (4%) cells with minimum T cell infiltration into the tumors. The overall immune profile is suggestive of a non-immunogenic model.
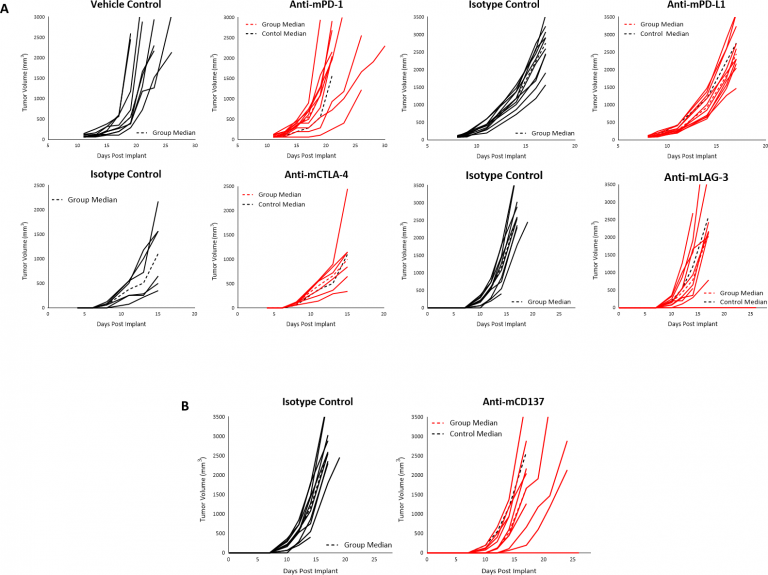
B16-F10 Response to Therapy
免疫调节剂:
在景气中,我们研究了该模型中的许多免疫调节抗体。当肿瘤达到〜90mm时的治疗开始3.检查点抑制剂anti-mPD-1或anti-mPD -L1 did not produce any response in subcutaneous B16-F10 tumors (Fig. 3A). Similarly, initiation of treatment with anti-mCTLA-4 or anti-mLAG-3 as early as four days post implant did not produce any response (Fig. 3A). Finally, we failed to see any anti-tumor activity when B16-F10 tumors were treated with the TNF receptor family co-stimulatory receptor CD137 (Fig 3B). Given the immune-suppressive tumor microenvironment of naïve B16-F10 tumors, it is not surprising that single agent immune modulators elicit limited/no response, and this lack of response suggests an immunologically cold tumor model, as has been reported for B16-F10.
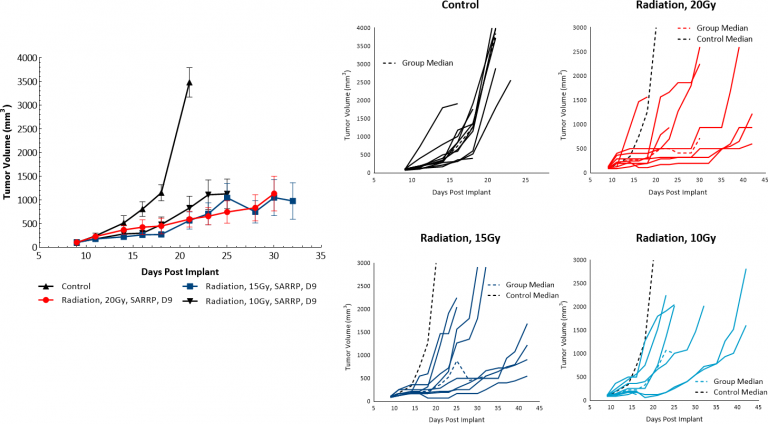
辐射:
放射治疗(RT)用于黑色素瘤病例,其中患者不是良好的手术候选人或拒绝手术治疗。我们评估了皮下B16-F10肿瘤与来自Xstrahl的小动物辐射研究平台(SARRP)输送的单剂量焦辐射的敏感性。10,15或20 Gy的放射治疗在至少50%的动物中显示出抗肿瘤活性,导致剂量反应肿瘤生长延迟为5.9,15和10.5天,分别显示B16-F10黑色素瘤模型对辐射响应(图4)。然而,甚至在测试的最高剂量的治疗均匀的治疗不会导致显着的回归或任何肿瘤的游离幸存者。因此,利用通过SARRP的焦点RT在临床前设定中yaboapp体育官网可以用于评估组合方法以模拟包括放射治疗的临床开发路径。
使用免疫调节剂和化学疗法或放射治疗的组合方法的黑素瘤患者的治疗选择是提高患者反应的潜在途径。[5]此外,组合治疗也可能有助于改变肿瘤的免疫感冒性朝向更容易接受的/反应性肿瘤微环境,这将变得更加敏捷。讨论B16-F10模型如何在您的下一次免疫疗法研究中有用,contact the scientists。
1https://www.skincancer.org/skin-cancer-information/melanoma/melanoma-warning-signs-and-images/。
2SEER癌症统计事实。国家癌症研究所,NIH(https://www.cancer.gov)。
3.NCI melanoma clinical trials (https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/clinical-trials/disease/melanoma).
4.nakamura k等人。实验转移模型对致命恶性肿瘤的小鼠黑素瘤细胞的特征。生活SCI。2002年1月4日; 70(7):791-8。DOI:10.1016 / S0024-3205(01)01454-0。
5.Schwartz Al等人。CD47的反义靶向增强人细胞毒性T细胞活性,并在与抗CTLA4和肿瘤照射结合时增加含B16黑色素瘤的小鼠的存活。癌症免疫接种。2019年10月18日。DOI:10.1007 / S00262-019-02397-7。
注意:研究是根据AAALAC认可的设施中适用的动物福利法规进行的