CT26-Luc:结肠癌原位小鼠模型:对免疫肿瘤学研究的启示
介绍
利用免疫系统的内在抗肿瘤活性来对抗癌症的治疗方法的出现代表了肿瘤治疗学的范式转变,它永久性地改变了我们对抗癌症的未来。
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a major contributor to the whole of cancer as a disease, representing 10% of all cases of cancer; over one million new cases of CRC were observed worldwide in 2018 resulting in over half a million deaths1. Clinical treatments involve surgical resection followed by adjuvant chemotherapy for non-metastasized colon cancer with more targeted therapies employed for metastatic CRC2. 最近的临床研究表明,免疫检查点抑制在治疗不可切除、转移性高微卫星不稳定性(MSI-H)或错配修复缺陷型(dMMR)结直肠癌中有很强的效果3. 临床获益如此之多,以至于Keytruda(针对人PD-1免疫检查点蛋白的单克隆抗体)在2020年夏天被批准作为满足这三个标准的大肠癌患者的一线治疗4. With this new promise of immunotherapy against CRC, highly translational preclinical models of the disease are required to assess the effectiveness of novel immuno-oncology agents.
评估以免疫系统为靶点的治疗药物的疗效需要具有完整免疫系统的临床前肿瘤模型,以供试验药物操作。同基因肿瘤模型代表了这样一种策略,在这种策略中,小鼠源性癌yaboapp体育官网细胞在肿瘤细胞起源的具有免疫活性的小鼠株中生长形成肿瘤。我们广泛使用CT26.WT小鼠结肠癌作为雌性Balb/c小鼠皮下肿瘤模型,以评估免疫肿瘤药物的疗效-见我们之前在模型聚光灯下的工作(如有要求,可提供额外数据):
We recognize the experimental and translational limitations of subcutaneous tumor models of holding a different tumor microenvironment compared to tumors rising from the organ of origin including, but not limited to, disparate immune cell profiles that can affect response to immunotherapy5,6. 将肿瘤细胞植入原始组织,称为原位肿瘤植入物,旨在纠正皮下研究的局限性,增加模型的潜在可移植性。
In this model spotlight we will provide data that demonstrate a robust and reproducible orthotopic murine tumor model utilizing CT26.WT colon carcinoma, reliable surgical methods for implantation and validating response to checkpoint inhibition.
All animal work was approved by the site Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and was performed in conformance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals within an AAALAC-accredited program with humane euthanasia criteria predetermined on all studies.
CT26.WT-luc肿瘤的原位生长
为了能够在原位纵向评估肿瘤进展,稳定转染CT26.WT小鼠结肠癌细胞以表达萤火虫荧光素酶,该酶能够通过生物发光成像(BLI)无创监测生长。不适用ï将所得CT26.WT-luc细胞接种于ve Balb/c小鼠皮下,建立皮下肿瘤模型。皮下肿瘤被切除并切割成碎片,移植到大鼠盲肠上ï由Fiegle et al。7从肿瘤植入后三天开始,每周两次对小鼠进行为期四周的BLI肿瘤生长评估,以纵向监测肿瘤生长(图1)。记录体重、每日临床观察和终末尸检观察。
图1 CT26.WT-luc衍生肿瘤原位植入Balb/c小鼠的生长动力学

的肿瘤负荷是抢劫ust and minimally variable. The tumor engraftment rate was 95% based on BLI and necropsy, no spontaneous regressions were observed. The BLI derived tumor volume doubling time (Td) was 1.5 days and the median time on study was 21 days.
与疾病进展相关的常见临床观察是肿瘤生长和体重增加引起的腹胀(数据未显示)。尸检显示盲肠有大的原发性肿块,肝脏和腹壁有小结节。结肠上的原发性肿瘤与结肠有较大的血管整合,表明肿瘤有效地招募血管。我们的下一个方法是利用这个模型来确定免疫肿瘤药物的疗效。
Checkpoint inhibition in the orthotopic CT26.WT-luc tumor model
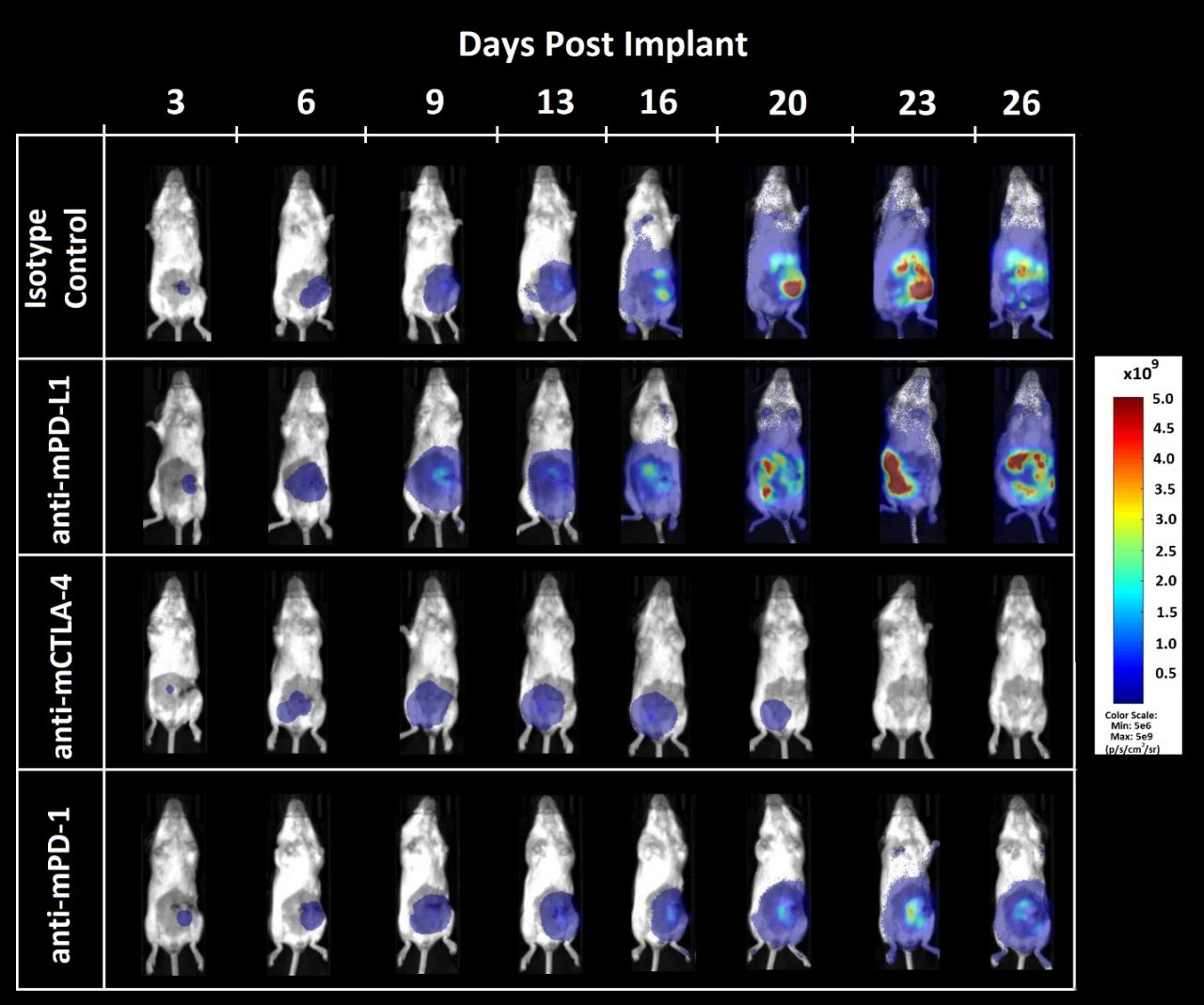
Naïve Balb/c mice were subjected to surgical implant of CT26.WT-luc tumor fragments as described previously. Animals were staged by BLI three days following surgery and distributed into treatment groups based on BLI values. Animals were treated by intraperitoneal administration of 10mg/kg isotype control (clone LTF-2), anti-mPD-L1 (clone 10F.9G2), anti-mCTLA-4 (clone 9D9) or anti-mPD-1 (clone RMP1-14) twice weekly for two weeks. All antibodies were acquired from BioXCell (Lebanon, New Hampshire, USA). Animals were monitored by twice weekly BLI measurements for tumor burden, three times a week collection of bodyweights, daily clinical observations, and terminal necropsy observations.
同型对照抗体的施用对肿瘤负担或疾病进展没有影响(图2A,2B)。同型对照组动物的肿瘤倍增时间为2.2天,研究中位时间为28天。服用抗mPD-L1(图2A,2C)导致一次完全消退(没有检测到高于背景BLI值的肿瘤负荷)。抗mCTLA-4治疗(图2A,2D)导致第23天ΔT型/ΔC为0.1%,5次部分回归(BLI值小于治疗第一天的一半),尸检时未发现明显疾病。抗-mPD-1(图2A,2E)的施用并未导致退化或无肿瘤存活者。
Figure 3. Bioluminescence imaging of CT26.WT-luc orthotopic tumor response to checkpoint inhibition
肿瘤负荷局限于腹部,并随着时间的推移而增加(图3),根据先前的试验性生长实验(数据未显示)。抗mCTLA-4治疗导致疾病相关体重增加的延迟发生(数据未显示)。抗mPD-L1或抗mCTLA-4的给药分别比同型对照组的12.5天和23.6天延长寿命。晚期尸检显示,8只服用抗mPD-L1的动物中有1只和8只服用抗mCTLA-4的动物中有5只没有肿瘤或其他病变的迹象。
Ongoing work is evaluating the differences between subcutaneous and orthoptic CT26.WT implant locations with respect to tumor immune cell infiltrate, histologic characteristics and morphology, along with immunologic activation in response to checkpoint blockade.
综上所述,我们已经证明CT26.WT-luc结肠癌原位模型为在高度平移的植入位置评估免疫肿瘤药物提供了一个强大的平台。联系我们的科学家to learn more about the CT26.WT-luc, and other murine orthotopic tumor models, and how we can apply these tools to advance your oncology pipeline.
References
1Bray F等,《2018年全球癌症统计:全球对185个国家36种癌症发病率和死亡率的估计》。CA癌症临床杂志2018;68:6, 394-424.
2Kuipers E等,结直肠癌。国家版次。2015; 1: 15065.
3Tintelnot J,Stein A。结直肠癌的免疫治疗:可用的临床证据、挑战和新方法。世界胃肠病学杂志。2019; 25:29, 3920-3928.
4食品和药物管理局。FDA批准初步ine immunotherapy for patients with MSI-H/dMMR metastatic colorectal cancer. Press Release, June 29 2020.
5Devaud C, et al. Tissues in different anatomical sites can sculpt and vary the tumor microenvironment to affect responses to therapy. Mol Ther. 2014; 22:1, 18-27.
6赵X,李L,斯塔尔TK,Subramanian S。肿瘤位置对结肠癌小鼠模型免疫反应的影响。2017年目标;8:33, 54775-54787.
7Fiegle E,Doleschel D等。双重CTLA-4和PDL-1阻断剂抑制高侵袭性原位结肠癌小鼠模型的肿瘤生长和肝转移。肿瘤形成;21:9, 932-944.
AUTHOR:
Patrick Allison,博士,科学发展科学家
日期:
December 2020